The waste of resources
The waste of resources is an additional waste for the seven wastes (muda) of lean manufacturing, it is the non efficient use of your lights, heat and power. This waste is a common waste in many organizations with employees often doing at work what they would never do at home. Would you leave lights on all day and night in unoccupied rooms at home or leave windows open in heated areas, you probably would not at home but many do at work; because they don’t pay the bills.
The costs of the waste of resources
If you leave on lights when no one is in the room, or leave machines idling whilst they are not in use and so on you will be using electricity. Each small failure to turn something off when not in use could cost you a small fortune on your electricity bills. With the rising utility costs this can mount up to a significant sum over the period of a year.
In the same way that you waste electricity, people will often leave water running and use far more than is necessary.
Heating (cooling if you live somewhere hot) is another area that costs your business a significant amount of money, but how often do you see windows or doors wide open allowing the hot air to escape, you then have to pay to reheat!
We also do not always consider the running costs of much of our equipment when we make purchases; usually we will look at the purchase price and think little of how much it will cost to run. But often for a small increase in the purchase price we can find more efficient equipment and machines that will reduce your utility bills significantly.
Causes of the Waste of resources.
Education and awareness is a major cause of this waste, people just do not always consider how much electricity/gas/water is wasted by their actions. Thus doors are left open, lights switched on, and taps are left running, things that many people now would not do at home, after all they have to pay the bills.
Policies for purchasing drive the company towards choosing the cheapest product rather than the most efficient.
Examples of wastes of resources
- Lights left on in empty rooms.
- Lights on when there is sufficient daylight.
- Doors and windows open allowing heat (cool air) to escape.
- Appliances left on standby (even mobile phone chargers continue to use electricity when not in use)
- Computers left on 24hours per day seven days a week.
- Machines left running when not in use.
How to eliminate or reduce resources
Educate your workforce to turn off lights and taps and keep doors and windows shut to retain hot or cold air.
Install timers and sensors on lights so that they are switched automatically. Install taps that turn themselves off after a few seconds.
Use automatic doors to ensure only open when people / vehicles passing.
Review thermostat settings to ensure that rooms are not overheated or cooled.
Review purchasing policies to consider life cycle costs of equipment not just the initial purchase price of the item.
Review the efficiencies of current equipment and see if replacement with more efficient equipment is justified.
Increase Profit through waste waste reduction.
For every penny you save in conserving your resources you can add one back to your profit, eliminating the causes of muda, mura and muri using lean principles can help you realise the benefits of lean manufacturing. By the implementation of lean manufacturing you can prevent the seven wastes of lean and increase your profits allowing you to compete successfully in this global market;
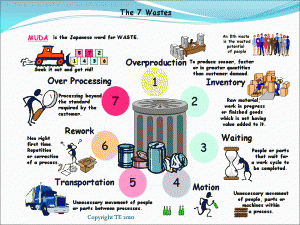
- The waste of inventory is the failure to reduce the raw materials, work in progress and finished stock that you hold.
- Thewaste of waiting is not ensuring that materials, instructions, and information arrive in a timely manner.
- The waste of Motion is the failure to ensure an efficient and ergonomic workspace.
- The waste of Overproduction is the production of product in either greater quantities than the customer needs or in advance of need.
- The waste of Overprocessing is adding more value to a product than is required.
- The waste of Defects is the occurrence of errors in your products or service.
- The waste of creativity is the failure to respect and involve your employees.
- The waste of Transport is the transportation of product from one location to another.